[ad_1]
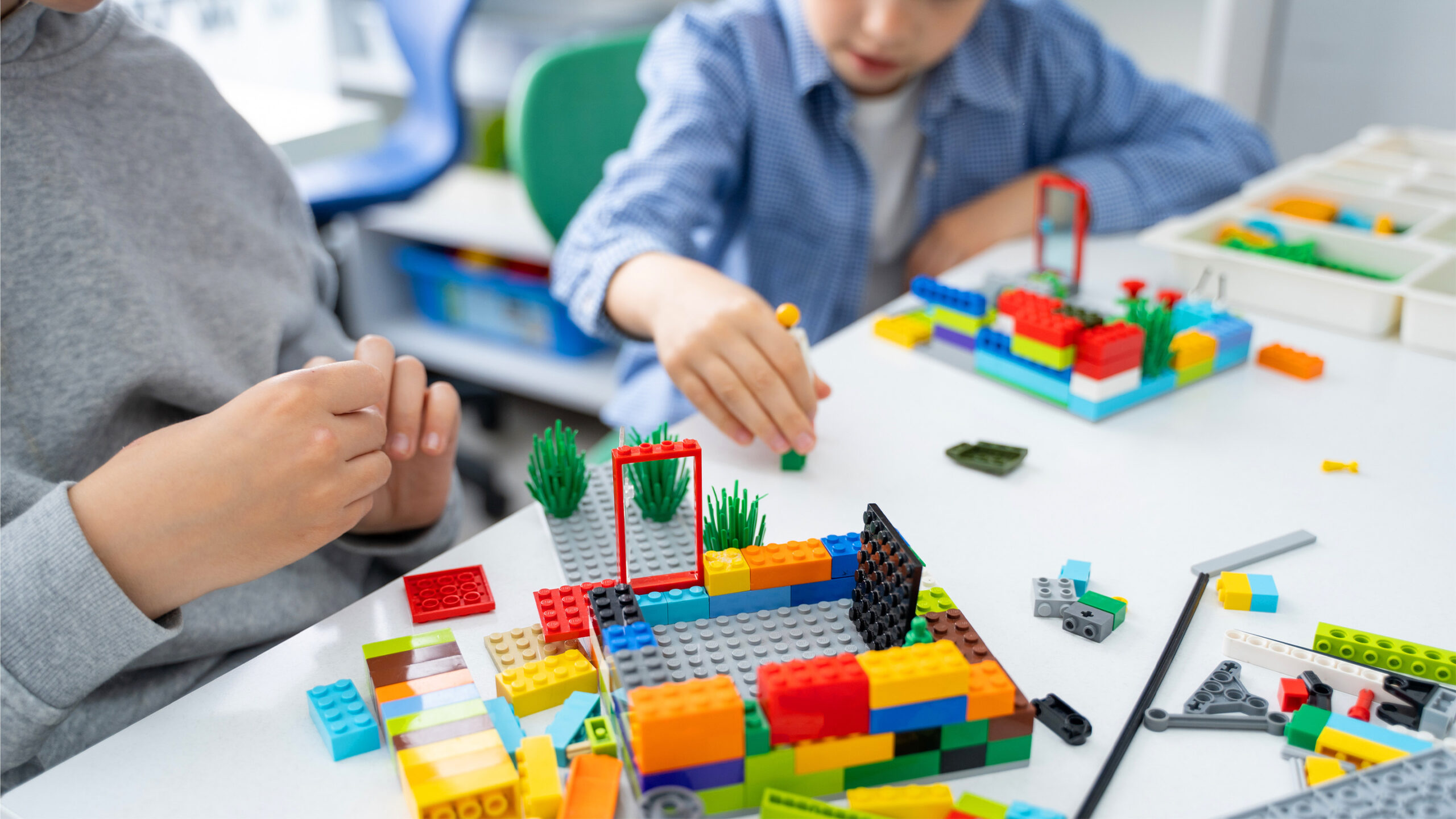
“Mrs. Dailey, it doesn’t know what Minecraft is!” The shocked voice of a fourth-grade boy rang out in shock and frustration. All through the room, eyes widened as school college students waited for my response. That they had been part of an after-school Lego membership the place I had decided to aim an experiment: Could I introduce elementary school college students to artificial intelligence (AI) in such a fashion that they could come to see it as a affiliate in project-based learning (PBL)?
I rigorously chosen school college students who had been loath to work with a human affiliate in years earlier, the students who would reasonably finish your full problem alone. After receiving appropriate consent, I had a bunch of lone wolves from first by way of fifth grades. Wonderful!
Getting Started
We dipped our toes into the AI world with Brickit, a free app that makes use of AI to analysis a pile of Lego bricks and generate builds with step-by-step instructions. All through this part, my school college students obtained right here to see AI as a software program to help them inside the establishing course of.
My school college students rapidly realized, nonetheless, that the AI did not understand their questions. Not solely did the AI not know what Minecraft was, it did not acknowledge Harry Potter or the Transformers, each. We shortly moved to an AI art work generator at neural.love.
Trying One different Technique
Using neural.love, we labored to engineer good prompts, nonetheless we had been moreover designing the framework for our AI-assisted Lego workforce assemble. After just some trials with producing a steady quick and generated image, my school college students constructed shut approximations of the imaginative and prescient they’d cocreated. We then decided to utilize the skills we had acquired to do a bunch problem partnering with ChatGPT.
The first stage of our framework was to establish a base vocabulary for the problem. Using the questions below, we generated a list of phrases we felt AI would need to know to understand our quick.
1. What vocabulary will biggest speak our thought?
2. If each phrase is perceived individually, will the question convey the mistaken thought?
3. What vocabulary may presumably be misleading, and why?
After determining that our problem might be a cityscape, we added to our vocabulary guidelines. We moreover started a collected vocabulary guidelines, which included phrases generated by ChatGPT that the students would possibly reuse, along with new phrases they needed to stipulate.
I left our guidelines by the laptop, and since the school college students collaborated, they launched phrases to me for the guidelines. I would ask them why we might have preferred to assemble each of the phrases, help them define unfamiliar phrases, and even retire redundant phrases.
Transferring to the Prompting Part
Throughout the prompting stage of our framework, we began to include ChatGPT as an exact affiliate by asking it the equivalent questions we had been asking each other. Proper right here, we centered intently on quick design.
1. Is that this quick too large/slender?
2. If that is the case, how can I widen/slender it?
3. Does it assume the AI has background information?
Lastly, we submitted the quick, “We need to assemble our metropolis with 5 huge sections which could be associated. What do you counsel for each half?” ChatGPT gave us a list with a brief description of each house.
Occurring to the Subsequent Step
Curating, which is the tactic of selecting, organizing, presenting, and taking good care of devices in a set, was the following stage of our framework. To curate our assortment of ideas, we might have preferred to dialogue with all of our companions, human and AI.
Each builder drew a design based mostly totally on their collected ideas. The quick “What buildings might be inside the downtown district?” gave one pupil a clear picture that he would possibly work with, whereas one different pupil spent a serious time period prompting and re-prompting for the details of life like apply tracks.
When their designs had been finalized, we moved into the creating stage, and afterward we moved fluidly between prompting, curation, and creation in the direction of our closing iteration of the assemble.
Encountering an Obstacle
Abruptly, we ran into a serious disadvantage. Each pupil was establishing their half on an entirely fully totally different scale. The apply tracks had been larger than the houses, and the skyscrapers had been shorter than the statues. The roads diversified in measurement and configuration. One pupil noticed these discrepancies and designed this quick, “How do I make the residential neighborhood to scale?”
ChatGPT’s reply produced further questions, which caught the attention of the other workforce members. Shortly, they’d been all crowded throughout the laptop computer with partial builds of their palms evaluating and contrasting. Lastly, they chose microscale and adjusted their builds to adapt.
Collaborating to a Conclusion
All through this stage, I watched my explicit particular person creators develop right into a workforce. Earlier to this, the students would each accumulate provides and work alone at fully totally different tables in silence. After the scale disaster, they moved their builds to the equivalent desk so that they could study sizes. This led to discussions and adjustments being made, further prompting to ChatGPT, and even co-building. We requested ourselves the subsequent questions:
1. Does the assemble resemble the distinctive thought, or has it modified?
2. If that is the case, whose enter launched the change?
3. Do you similar to the changes?
4. If not, what can you do to shift the problem once more on monitor?
My school college students confessed that they’d all modified their assemble based mostly totally on the enter of their human and AI companions, and as they moved forward, they’d been pleased with the changes.
After we reached a consensus, the last word stage of our framework was strategies. On this stage, we helped ChatGPT develop as a result of it realized regarding the outcomes we achieved. After we fitted the completed sections collectively and made just some closing tweaks, we described our accomplished product to ChatGPT and obtained its congratulations.
The students had been elated with this closing little little bit of dialogue, they normally all expressed the idea their AI affiliate was invaluable and had an enormous physique of information to ship to the desk. They concluded that consulting with AI was a kick off point for a problem, reasonably than a provide for a accomplished product.
Lastly, they reported that their creativity was enhanced by all companions. As a workforce, they labored with plenty of varied sorts of AI and helped create a replicable framework for partnering with AI. In the long term, they achieved an revolutionary problem that enhanced their learning, technological, and interpersonal skills.
For me as an educator experimenting with new know-how, it’s gratifying to facilitate a bunch of students coming collectively to complete a protracted problem. Watching this group of solitary builders solidify proper right into a workforce working with their mates and a sophisticated artificial intelligence to create a superior product was actually rewarding. I take into consideration this experiment a success, as a result of the group clearly obtained right here to deal with AI as a affiliate of their project-based learning, and I am pleased with their effort, their closing product, and the framework we created collectively.
[ad_2]
Provide hyperlink













Leave a Reply